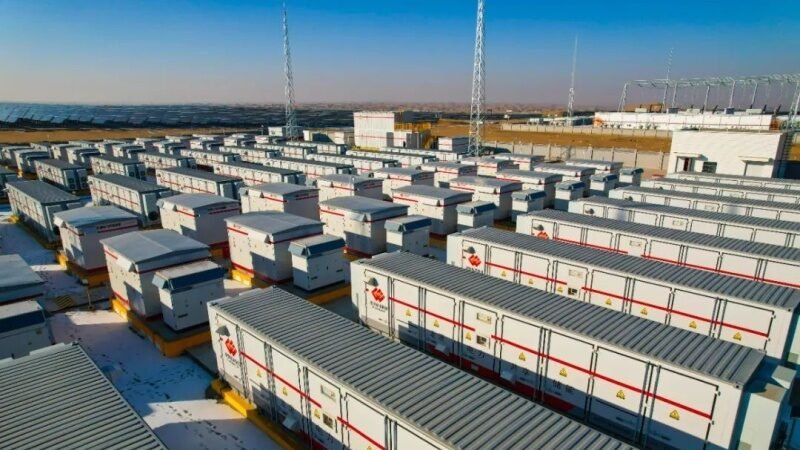
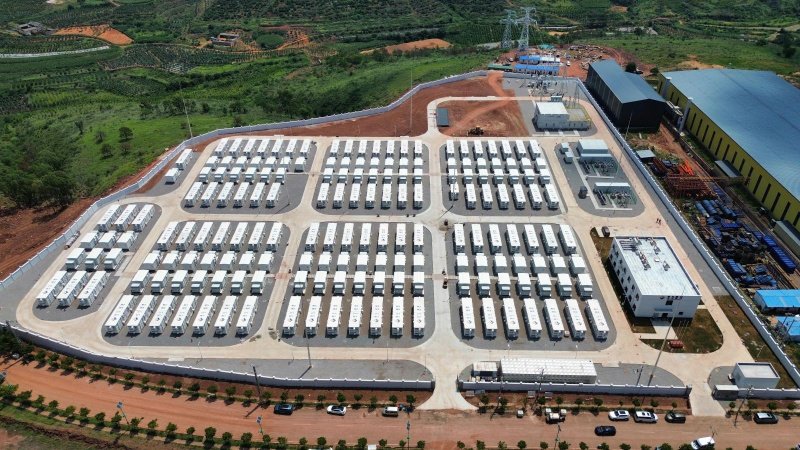
Located in the vast Tengger Desert of Ningxia, this project combines a 100 MW photovoltaic plant with a 200 MWh energy storage system, forming one of the most representative cases of large-scale solar development in arid regions. The integration of energy storage was a key design consideration from the outset, ensuring that clean solar power could be delivered not only when the sun shines but also during evening and nighttime peak hours, when demand is highest.
The project significantly improves the flexibility and reliability of renewable generation. By capturing excess daytime output and releasing it later, the storage system reduces curtailment and stabilizes the local grid, which is often challenged by fluctuating solar resources in remote areas. This enables the Tengger Desert project to play a dual role: generating clean electricity and actively supporting grid regulation through peak shaving and load balancing.
Beyond its technical merits, the project also demonstrates the environmental and strategic value of clean energy in desert regions. It makes use of barren land that has little alternative economic value, while avoiding competition with agriculture. At the same time, it contributes to carbon reduction goals and serves as a model for how large-scale solar and storage can transform underdeveloped areas into hubs of renewable power. The success of this initiative provides valuable experience for future deployments across China’s deserts and other challenging terrains worldwide.